Directions (1-5): Study the following information carefully and answer the given questions:
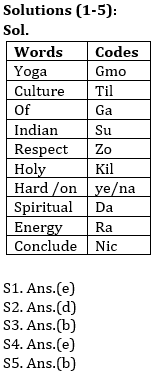
In a certain code language
‘yoga of Indian culture’ is written as `ga gmo til su’
‘hard respect yoga holy on’, is written as ‘kil zo gmo ye na’
‘culture respect spiritual energy’ is written as `zo ra til da’
‘spiritual conclude of holy’ is written as `da ga nic kil’.
Q1. What is the code for ‘on’?
(a) ye
(b) na
(c) zo
(d) Either na or zo
(e) Either ye or na
Q2. What does `su’ stand for?
(a) culture
(b) yoga
(c) of
(d) Indian
(e) None of these
Q3. What is the code for ‘energy yoga conclude’?
(a) nic ye til
(b) gmo ra nic
(c) ra ga gmo
(d) da ra nic
(e) None of these
Q4. Which of the following does `kil til na’ stand for?
(a) holy of yoga
(b) hard yoga holy
(c) culture holy hard
(d) culture holy on
(e) Either (c) or (d)
Q5. Which of the following may represent ‘record rate of yoga’?
(a) ga zo til da
(b) ga ba gmo nee
(c) ga ba nic kil
(d) gmo ba til ra
(e) None of these
Directions (6-10): Study the following information carefully and answer the given questions:
Give answer-
(a) if only conclusion I is true.
(b) if only conclusion II is true.
(c) if either conclusion I or II is true.
(d) if neither conclusion I nor II is true.
(e) if both conclusions I and II are true.
Q6. Statements: L ≤ K, K <M, J ≥M
Conclusions:
I. L < M
II. K < J
Q7. Statements: E ≤ W, W < Q, Q ≥ H
Conclusions:
I. E ≤ Q
II. E =H
Q8. Statements: J = T, T > W, W ≥ R
Conclusions:
I. J > R
II. T ≥R
Q9. Statements: T > R, R ≥ H, H < F
Conclusions:
I. H < T
II. F = T
Q10. Statements: F = D, D > V, V < P
Conclusions:
I. F = P
II. V > F
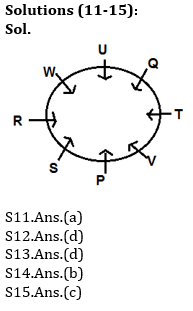
Directions (11-15): Study the following information carefully to answer the given questions.
There are eight employees i.e. P, Q, R, S, T, U, V and W who have decided to do the lunch in Restaurant. They have seated around a circular table and facing towards the centre but not necessarily in the same order. T sits 2nd right of P.R is not an immediate neighbour of P and T. S is not an immediate neighbour of W. There are two employees between R and Q who sits 2nd left of W. W sits opposite to V who is an immediate neighbour of both P and T.
Q11. Who among the following sits immediate left of V?
(a) P
(b) S
(c) T
(d) U
(e) None of these
Q12. How many employees sit between S and T, clockwise counting from S?
(a) Two
(b) Five
(c) One
(d) Four
(e) No one
Q13. Who among the following sits immediate left of S?
(a) V
(b) U
(c)Q
(d) R
(e) T
Q14. Who among the following sits 2nd to the right of R?
(a) U
(b) P
(c) V
(d) W
(e) None of these
Q15. If Q is related to S and T is related to R, then U is related to which employee?
(a) V
(b) Q
(c) P
(d) W
(e) None of these
Solutions







 General Awareness Quiz for Bank Mains Ex...
General Awareness Quiz for Bank Mains Ex...
 English Language Quiz For Bank Foundatio...
English Language Quiz For Bank Foundatio...
 Reasoning Quiz For Bank Foundation 2024 ...
Reasoning Quiz For Bank Foundation 2024 ...









