Q1. Manoj’s monthly salary is 25% more than Mohit’s salary. Mayank’s monthly salary is Rs 1750 more than Mohit’s monthly salary. Sum of Manoj’s, Mayank’s and Mohit’s yearly salary is Rs 3,33,000.
Quantity I: Sum of monthly salary of Manoj and Mohit together
Quantity II: Rs. 20,000
![]()
(a) Quantity I > Quantity II
(b) Quantity I < Quantity II
(c) Quantity I ≥ Quantity II
(d) Quantity I ≤ Quantity II
(e) Quantity I = Quantity II or No relation

Q3. Quantity I: Profit share of ‘A’ out of total annual profit of Rs. 56,500. A, B and C enter into a partnership. ‘A’ invests Rs. 4000 for the whole year, ‘B’ puts in Rs. 6000 at the first and increasing to Rs. 8000 at the end of 4 months, whilst C puts in at first Rs. 8000 but withdraw Rs. 2000 at the end of 9 months.
Quantity II: Amount which when lend on C.I. at 20% interest being compounded annually for 3 years, gives total interest equal to Rs.9100
(a) Quantity I > Quantity II
(b) Quantity I ≥ Quantity II
(c) Quantity I < Quantity II
(d) Quantity I = Quantity II or No relation
(e) Quantity I ≤ Quantity II
Q4. 8 men and 4 women together can complete a piece of work in 6 days. Work done by a man in one day is double the work done by a woman in one day. 8 men and 4 women started working and after 2 days, 4 men left and 4 new women joined the work.
Quantity I: More days required to complete the work
Quantity II: 5 days
(a) Quantity I = Quantity II or No relation
(b) Quantity I ≥ Quantity II
(c) Quantity I < Quantity II
(d) Quantity I ≤ Quantity II
(e) Quantity I > Quantity II
Q5. The ratio of the age of Tina and Rakesh is 9 : 10 respectively. Ten years ago the ratio of their age was 4 : 5 respectively.
Quantity I: 22 years
Quantity II: Present age of Rakesh
(a) Quantity I > Quantity II
(b) Quantity I < Quantity II
(c) Quantity I = Quantity II or No relation
(d) Quantity I ≥ Quantity II
(e) Quantity I ≤ Quantity II
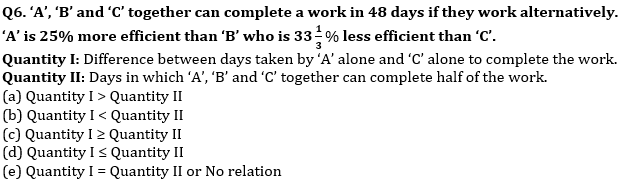
Q7. Neeraj invested Rs. X in two different schemes ‘A’ and ‘B’ equally. Scheme A offers 10% p.a. at S.I and scheme B offers 20% p.a. at C.I. After 2 years he got total Rs.2560 interest from both the schemes.
Quantity I: Value of ‘X’
Quantity II: Rs. 7200
(a) Quantity I ≥ Quantity II
(b) Quantity I = Quantity II or No relation
(c) Quantity I > Quantity II
(d) Quantity I ≤ Quantity II
(e) Quantity I < Quantity II
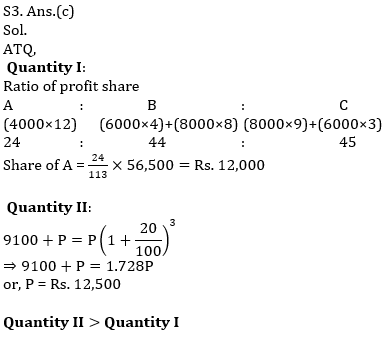
Q8. Three partners invested capital in the ratio 2 : 7 : 9. The time period for which each of them invested was in the ratio of the reciprocals of the amount invested..
Quantity I: Profit share of the partner who brought in the highest capital if the profit is Rs. 1080
Quantity II: Profit share of the partner who brought in the lowest capital if the profit is Rs. 1080
(a) Quantity I > Quantity II
(b) Quantity I ≥ Quantity II
(c) Quantity I < Quantity II
(d) Quantity I = Quantity II or No relation
(e) Quantity I ≤ Quantity II
Q9. X started from a point A towards point B. After 2 hours. Y started from B towards A. By the time X travelled one-fifth of the total distance, Y had also travelled the same. Y’s speed is thrice of that of X’s speed.
Quantity I: Difference in time (in hours) taken by X and Y to reach their respective destinations.
Quantity II: 12 hours
(a) Quantity I = Quantity II or No relation
(b) Quantity I ≤ Quantity II
(c) Quantity I ≥ Quantity II
(d) Quantity I < Quantity II
(e) Quantity I > Quantity II
Q10. A vessel contains 2.5 litres of water and 10 litres of milk. 20% of the contents of the vessel are removed. To the remaining contents, x litres of water is added to reverse the ratio of water and milk. Then y litres of milk is added again to reverse the ratio of water and milk.
Quantity I: Value of ‘y’
Quantity II: Value of ‘x’
(a) Quantity I = Quantity II or No relation
(b) Quantity I ≤ Quantity II
(c) Quantity I ≥ Quantity II
(d) Quantity I < Quantity II
(e) Quantity I > Quantity II
Solutions





Click Here to Register for Bank Exams 2021 Preparation Material




 IDBI Bank Recruitment 2026 Notification ...
IDBI Bank Recruitment 2026 Notification ...
 SBI CBO Admit Card 2026 Out at sbi.co.in...
SBI CBO Admit Card 2026 Out at sbi.co.in...
 SBI Clerk Mains Scorecard 2025-26 Out @S...
SBI Clerk Mains Scorecard 2025-26 Out @S...









