Preparing for the Union Bank Specialist Officer (SO) exam requires a sharp focus on reasoning skills, as this section is essential for clearing the written stage. To help candidates strengthen their logical thinking, pattern recognition, and analytical abilities, we have compiled a Union Bank SO Reasoning Practice Set with detailed answers. These questions reflect the exam-level difficulty and aim to improve both accuracy and speed. Attempting such practice sets regularly can boost your confidence and familiarity with the exam format.
Union Bank SO Reasoning
The practice set for the Union Bank SO Reasoning section is curated to reflect the latest exam trends, difficulty level and variety of questions that typically appear in the exam. It includes a range of topics such as puzzles, seating arrangements, blood relations, coding-decoding, input-output, syllogisms, inequality, direction sense, and logical reasoning. Each question is designed not only to test your understanding but also to train you in time management and problem-solving techniques under pressure.
Tips to Prepare for Reasoning for Union Bank SO
To ace the reasoning section of the Union Bank SO exam, you need a strategic approach that focuses on mastering the basics and practising regularly. Consistent effort combined with the right techniques can help you tackle even the trickiest questions with ease. Here are some key tips to boost your preparation:
- Understand the Exam Pattern: Know the types of reasoning questions asked, such as puzzles, seating arrangement, syllogism, input-output, etc.
- Master the Basics First: Strengthen your foundational concepts in topics like blood relations, direction sense, coding-decoding, and inequalities.
- Practice with Timed Sessions: Solve mock tests and practice sets in a timed manner to improve your speed and accuracy.
- Work on Visualization: For puzzles and seating arrangements, practice drawing clear diagrams for better understanding.
- Revise Short Tricks & Formulas: Learn shortcut techniques for common reasoning problems to save time during the exam.
- Review Mistakes: Analyse your mock tests and learn from incorrect answers to avoid repeating them.
- Stay Consistent: Make reasoning practice a daily habit to build confidence and familiarity with question patterns.
Union Bank SO Practice Set- Reasoning (With Answers)
Directions (01-03): In these questions, relationships between different elements are shown in the statements. The statements are followed by two conclusions. Study the conclusions based on the given statements and select the appropriate answer:
Q01. Statements: A ≥ B < C = D > E ≥ F = O, G ≥ H = I > J ≥ N, K > L = J < M ≤ O = P
Conclusions: I. C > N II. L < B
(a) Only conclusion II is true
(b) Only conclusion I is true
(c) Either conclusion I or II is true
(d) Both conclusions I and II are true
(e) Neither conclusion I nor II is true
Q02. Statements: P > Q ≥ R ≥ S = T < V, U ≥ V = W ≥ X, N < W = Y < Z ≤ T
Conclusions: I. X ≤ Q II. V > N
(a) Both conclusions I and II are true
(b) Only conclusion II is true
(c) Either conclusion I or II is true
(d) Neither conclusion I nor II is true
(e) Only conclusion I is true
Q03. Statements: M < N ≤ O = P ≥ Q = R > S ≥ T, L ≤ W < U < O, V > W ≤ X = Y = A < B
Conclusions: I. Y ≥ P II. P > Y
(a) Either conclusion I or II is true
(b) Neither conclusion I nor II is true
(c) Only conclusion I is true
(d) Only conclusion II is true
(e) Both conclusions I and II are true
Directions (04-08): Study the following information carefully and answer the given questions:
Twelve persons- J, K, L, M, N, O, P, Q, R, S, T and U are living in the six-floor building (but not necessarily in the same order). The ground floor is numbered as 1, the floor just above it is numbered as 2 and so on. Each floor has 2 flats in it i.e., Flat X and Flat Y. Flat X of floor 2 is immediately above flat X of floor 1 and immediately below flat X of Floor 3. Flat Y of Floor 2 is immediately above flat Y of floor 1 and immediately below flat Y of Floor 3. Flat X is exactly to the west of Flat Y.
M lives on an even number floor but not in flat X. Two floors are there between the floor on which M and K lives. K doesn’t live in flat Y. O lives immediately above K in the same named flat. O lives southwest of J who lives below M. Q lives immediately above S in the same named flat. S doesn’t live on first and fifth floor. T lives west of U and northwest of N. Neither U nor N lives above J. R lives on the floor immediately above L.
Q04. In which among the following floor does O lives?
(a) Second floor
(b) First Floor
(c) Either first or third floor
(d) Fourth floor
(e) None of these
Q05. Who among the following person lives in flat X on the third floor?
(a) S
(b) The person who lives northwest of J.
(c) The person who lives exactly to the west of S.
(d) T
(e) None of these
Q06. Who lives immediately above S in the same named flat?
(a) One who lives east of L
(b) O
(c) U
(d) M
(e) None of these
Q07. How many floors are there between the floors in which M and N live?
(a) One
(b) Two
(c) Three
(d) Four
(e) Either two or four
Q08. Who among the following person lives on sixth floor in Flat X?
(a) The one who lives immediately above J in the same named flat.
(b) L
(c) The one who lives to the west of M.
(d) O
(e) None of these
Directions (09-11): Study the following information carefully and answer the given questions:
A&B means A is mother of B
A*B means A is child of B
A%B means A is parent of B
A!B means A is sibling of B
A#B means A is daughter-in-law of B
A@B means A is husband of B
Q09. In the 5 members of family, If ‘K#L@M&N%O’ is true, then how is L related to O?
(a) Father
(b) Grandmother
(c) Cousin
(d) Grandfather
(e) None of these
Q10. If ‘X@Y*Z@W&M’ is true, then how is W related to sister of M?
(a) Aunt
(b) Niece
(c) Daughter
(d) Sister
(e) Mother
Q11. If ‘L@M&N!O@P’ is true, then how is P related to M?
(a) Mother
(b) Sister
(c) Daughter-in-law
(d) Mother-in-law
(e) Can’t be determined
Directions (12-16): Study the following information carefully and answer the questions given below:
Eight persons sit in two parallel rows. A, B, C, and D sit in row 1 and facing south direction. P, Q, R, and S sit in row 2 and facing north direction. Persons in both rows are facing each other. Each of them has currencies of different countries i.e. Dinar, Won, Peso, Pound, Euro, Real, Yen and Dollar.
C sits second to the right of the one who faces the one who has Won. Q neither has Dollar nor Dinar and sits second to the left of S. Q does not face immediate neighbours of C. One person sits between C and B who has Peso. The one who has Yen immediate neighbour of C and sits opposite to the one who has Euro. R sits second to the right of the one who has Euro. D does not sit opposite to R. The one who sits opposite to P sits second to the right of the one who has Real. Two persons sit between the one who has pound and the one who has Dollar.
Q12. Who among the following has Dinar?
(a) A
(b) C
(c) D
(d) P
(e) None of these
Q13. Who sits opposite to the one who has Dollar?
(a) The one who has Peso
(b) D
(c) C
(d) The one who has Real
(e) None of these
Q14. Who among the following sits diagonally opposite to R?
(a) A
(b) The one who has Dinar
(c) B
(d) The one who has Yen
(e) None of these
Q15. Four of the following five are alike in a certain way based on the given arrangement and thus form a group. Which of the following does not belong to that group?
(a) R
(b) Q
(c) A
(d) B
(e) C
Q16. Which of the following statement is false?
(a) C is not an immediate neighbour of A
(b) P does not sit opposite to B
(c) R does not have Pound
(d) D does not have Yen
(e) None of these
Directions (17-21): Study the following information carefully and answer the questions given below:
Eight persons i.e., C, D, E, M, J, K, L and P (but not necessarily in the same order) sit around a circular table such that some of them are facing inside and some of them are facing outside of the table.
E sits third to the right of D. D does not face towards the table. One person sits between E and J. L sits second to the left of J. C and P sit adjacent to each other. P does not sit adjacent to E and L. C and L do not sit adjacent to each other. M sits second to the left of C. M and P do not sit adjacent to each other. K sits third to the left of P. Both the immediate neighbours of C face in the opposite direction. M and J sit immediately right of each other. K and L face in the same direction as M.
Q17. Who sits immediately to the left of L?
(a) J
(b) K
(c) D
(d) P
(e) None of these
Q18. How many persons sit between D and M when counted from the right of D?
(a) Two
(b) Three
(c) One
(d) Four
(e) None of these
Q19. Who sits second to the left of K?
(a) E
(b) D
(c) M
(d) L
(e) None of these
Q20. What is the position of J with respect to D?
(a) Second to the right
(b) Immediately right
(c) Third to the left
(d) Second to the left
(e) None of these
Q21. Four of the following five are alike in a certain way, thus who among the following does not belong to that group?
(a) E
(b) M
(c) K
(d) L
(e) P
Q22. If it is possible to make only one meaningful word from the 3rd, 5th, 6th and 9th letters of the word “STRATEGIC” using each letter only once, then what is the last letter of the word. If no such meaningful word can be formed the answer is “X” and if more than one such meaningful word can be formed, the answer will be “Z”?
(a) E
(b) X
(c) T
(d) R
(e) Z
Q23. In the given word “ATTRACT” if the letters at the odd position when counts from the left are changed with their just succeeding letter according to alphabetical series and the letters at the even position when counts from the left are changed with their just preceding letter according to alphabetical series then how many letters are repeated in the word thus formed?
(a) Two
(b) One
(c) None
(d) Three
(e) Four
Q24. In the number ‘23859467, if the first half digits are added by 1 and the second half digits are subtracted by 2. Then, what will be the sum of all the odd digits of the new number formed after rearrangement?
(a) 22
(b) 23
(c) 24
(d) 26
(e) None of these
Directions (25-27): Study the following information carefully and answer the questions given below:
Point M is 3m to the west of Point N. Point N is 6m to the north of Point O. Point P is 8m to the east of Point O. Point Q is 10m south of Point P. The distance between Point R and Point Q is equal to the distance between Point O and Point P. Point Q is in the east of Point R. Point S is 6m to the south of Point R. Point T is 12m to the east of Point S.
Q25. What is the direction of Point M with respect to Point Q?
(a) North
(b) North-East
(c) North-West
(d) East
(e) None of these
Q26. What is the shortest distance between Point O and Point Q?
(a) √164m
(b) 12m
(c) √168m
(d) 13m
(e) None of these
Q27. What is the total distance from Point N to Point S?
(a) 39m
(b) 37m
(c) 38m
(d) 36m
(e) None of these
Q28. WHO says one in 10 children did not get vaccinated in 2016. Global health body worried about immunization levels. Despite immunization being one of the most successful and cost-effective means to help children grow into healthy adults, worldwide 12.9 million infants — nearly 1 in 10 — did not receive any vaccination in 2016. Which of the following can be inferred from the given statement?
(a) Immunization prevents illness, disability and death from vaccine preventable diseases.
(b) 104 children did not get vaccinated in 2016 out of total 1340 children.
(c) An additional 1.5 million deaths could be avoided if global immunization coverage improves.”
(d) Over the years, the positive trend “has been the increasing uptake of new and
underused vaccines”.
(e) Most of the children missing out are those living in the poorest, marginalized and conflict affected communities.
Q29. The Indian Ocean is the world’s biggest dumping ground for plastic waste, but where the trash ultimately ends up has remained a mystery, scientists say. According to researchers from the University of Western Australia (UWA), little research had been done to measure and track plastic waste in the Indian Ocean. Which of the following can be assumed from the given statement?
(I) Indian Ocean ultimately pushes floating plastics towards the western side of the ocean.
(II) It is also most likely that floating plastics will ultimately end up on beaches.
(III) Study shows that the atmospheric and oceanic attributes of the Indian Ocean are different to
other ocean basins.
(IV) There may not be a concentrated garbage patch for the accumulation of marine debris in India.
(a) Only I and IV are implicit
(b) Only III is implicit
(c) Only III and II are implicit
(d) None is implicit
(e) Only I, II and III are implicit
Q30. World’s forests are ‘in emergency room’. Study shows that the world lost 12 million hectares of tropical tree cover last year — the equivalent of 30 football pitches a minute — researchers said on Thursday, warning the planet’s health was at stake as we depend on forests for our survival from the air, we breathe to the wood we use and so on. Which of the following may be the reason of the warning given in the statement?
(I) Forests and trees make vital contributions to both people and the planet, bolstering livelihoods, providing clean air and water, conserving biodiversity and responding to climate change.
(II)How to increase agricultural production and improve food security without reducing forest area is one of the great challenges of our times.
(III)There is quantitative evidence to show that forests are being managed more sustainably.
(a) Only I is implicit
(b) Only III is implicit
(c) Only III and II are implicit
(d) None is implicit
(e) Only I, II and III are implicit
Directions (31-35): Study the following information carefully and answer the given questions:
Eleven people C, D, E, F, G, H, I, J, K, L and M were born in eleven different years but not necessarily in the same order. Their age is calculated from 2024 and they were born in 1985, 1988, 1989, 1991, 1992, 1993, 1994, 1995, 1999, 2000, and 2002.
Sum of ages of C and D is multiple of 20. Age of E is more than J but less than D. J was not born in 2002. Sum of ages of L and G is 58. Sum of ages of F and H is more than the sum of ages of H and K. H is not oldest person but older than K. L was born in Leap year. As many persons were born before L is same as were born after M. Four persons were born between M and I. The number of persons born before I is one more than the number of persons born after C.
Q31. Four of the following five pairs are in the same group, which among the following does not belong to that group?
(a) D
(b) L
(c) H
(d) C
(e) J
Q32. Who among the following was born in 1994?
(a) H
(b) J
(c) The one who was born immediately after D
(d) F
(e) The one who was born immediately before G
Q33. If the sum of ages of F and Z is 80 years then, what will be the age of Z?
(a) 45 years
(b) 40 years
(c) 42 years
(d) 41 years
(e) 46 years
Q34. How many persons were born between L and the one who was born immediately before M?
(a) 8
(b) 3
(c) 7
(d) 5
(e) 6
Q35. Who was born three persons after the one who was born just before L?
(a) H
(b) K
(c) I
(d) D
(e) E
| Answers | |||||||||
| 01 | 02 | 03 | 04 | 05 | 06 | 07 | 08 | 09 | 10 |
| b | b | e | d | c | e | d | c | d | e |
| 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 | 15 | 16 | 17 | 18 | 19 | 20 |
| c | b | d | b | d | d | b | b | c | c |
| 21 | 22 | 23 | 24 | 25 | 26 | 27 | 28 | 29 | 30 |
| a | b | a | c | c | a | c | a | d | a |
| 31 | 32 | 33 | 34 | 35 | |||||
| b | c | d | e | b | |||||
Answers
S01. Ans.(b)
Sol. I. C > N (True) II. L < B (False)
S02. Ans.(b)
Sol. I. X ≤ Q (False) II. V > N (True)
S03. Ans.(a)
Sol. I. Y ≥ P (False) II. P > Y (False)
Directions (04-08):
Final arrangement:
| Floors | Flat X | Flat Y |
| 6 | R | M |
| 5 | L | J |
| 4 | O | Q |
| 3 | K | S |
| 2 | T | U |
| 1 | P | N |
Clues: M lives on even number floor but not in flat X. Two floors are there between the floor on which M and K lives. K doesn’t live in flat Y. O lives immediately above K in the same named flat.
Inference: Here we get three possible cases-
| Floors | Case 1 | Case 2 | Case 3 | |||
| Flat X | Flat Y | Flat X | Flat Y | Flat X | Flat Y | |
| 6 | M | O | ||||
| 5 | K | |||||
| 4 | O | M | ||||
| 3 | K | |||||
| 2 | O | M | ||||
| 1 | K | |||||
Clues: O lives southwest of J who lives below M. Q lives immediately above S in the same named flat. S doesn’t live on first and fifth floor. T lives west of U and northwest of N. Neither U nor N lives above J.
Inference: Here case2 and case 3 will be eliminated and we get-
| Floors | Case 1 | Case 2 | Case 3 | |||
| Flat X | Flat Y | Flat X | Flat Y | Flat X | Flat Y | |
| 6 | M | O | ||||
| 5 | J | K | ||||
| 4 | O | Q | Q | M | ||
| 3 | K | S | S | J | ||
| 2 | T | U | O | M | ||
| 1 | N | K | ||||
Clues: R lives on the floor immediately above L.
Inference: After applying the above condition only place for P is left and the final arrangement is-
| Floors | Flat X | Flat Y |
| 6 | R | M |
| 5 | L | J |
| 4 | O | Q |
| 3 | K | S |
| 2 | T | U |
| 1 | P | N |
S04. Ans.(d)
Sol. O lives on the fourth floor.
S05. Ans.(c)
Sol. The person who lives exactly to the west of S lives in flat X on the third floor.
S06. Ans.(e)
Sol. Q lives immediately above S in the same named flat.
S07. Ans.(d)
Sol. Four floors are there between the floors in which M and N live.
S08. Ans.(c)
Sol. The one who lives west of M lives on sixth floor in flat X.
S09. Ans.(d)
Sol. L is grandfather of O.
S10. Ans.(e)
Sol. W is mother of sister of M.
S11. Ans.(c)
Sol. P is Daughter-in-law of M.
Solutions (12-16):
Final Arrangement:
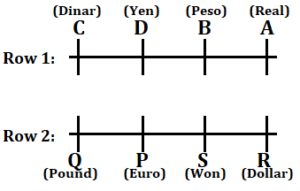
Clues: C sits second to the right of the one who faces the one who has Won. Q neither has Dollar nor Dinar and sits second to the left of S. Q does not face immediate neighbours of C. One person sit between C and B who has Peso.
Inferences: From these conditions there are two possibilities:
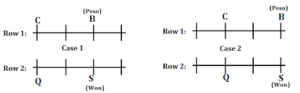
Clues: The one who has Yen immediate neighbour of C and sits opposite to the one who has Euro. R sits second to the right of the one who has Euro. D does not sit opposite to R.
Inferences: There is only possibility D has Yen currency.
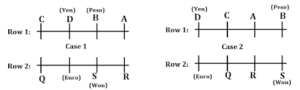
Clues: The one who sits opposite to P sits second to the right of the one who has Real. Two persons sit between the one who has pound and the one who has Dollar.
Inferences: From these conditions case 2 will be eliminated.
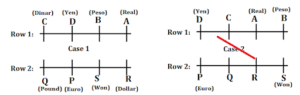
Inferences: The final arrangement is –

S12. Ans.(b)
Sol. C has Dinar.
S13. Ans.(d)
Sol. R has dollar and A who has real sits opposite to each other.
S14. Ans.(b)
Sol. C who has dinar sits diagonally opposite to R.
S15. Ans.(d)
Sol. Except B, all other persons sit at the ends of the rows.
S16. Ans.(d)
Sol. D has Yen.
Directions (17-21):
Final arrangement:
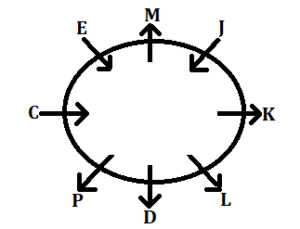
Clues: E sits third to the right of D. D does not face towards the table. One person sits between E and J. L sits second to the left of J.
Inference: From the above conditions there are two possibilities i.e., Case 1 and Case 2.
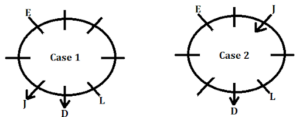
Clues: C and P sit adjacent to each other. P does not sit adjacent to E and L. C and L do not sit adjacent to each other. M sits second to the left of C. M and P do not sit adjacent to each other.
Inference: From the above conditions, it is clear that M and J sit adjacent to each other.
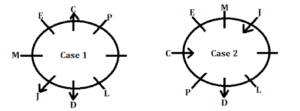
Clues: K sits third to the left of P. Both the immediate neighbours of C face in the opposite direction. M and J sit immediately right of each other. K and L face in the same direction as M.
Inference: From the above condition, case 1 is cancelled here as there is no place for K.
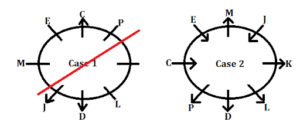
Inference: Final arrangement:

S17. Ans.(b)
Sol. K sits immediately left of L
S18. Ans.(b)
Sol. Three persons sit between D and M when counted from the right of D
S19. Ans.(c)
Sol. M sits second to the left of K
S20. Ans.(c)
Sol. J sits third to the left of D
S21. Ans.(a)
Sol. Expect for the person in option (a), all other persons face away from the table.
S22. Ans.(b)
Sol. 3rd, 5th, 6th and 9th letters of the word “STRATEGIC” are RTEC respectively.
There is no meaningful word is formed using RTEC.
S23. Ans.(a)
Sol. Word after changing letters is BSUQBBU
Two letters are repeated in the word i.e., B and U.
S24. Ans.(c)
Sol. The number after adding 1 in the first half and after subtracting 2 from the second half of the number is: 34967245
The sum of all the odd digits = 3+9+7+5 = 24
Directions (25-27):
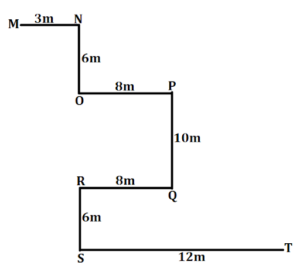
S25. Ans.(c)
Sol. Point M is in North-west of Point Q
S26. Ans.(a)
Sol. The shortest distance between Point O and Point Q is √164m
S27. Ans.(c)
Sol. The total distance from Point N to Point S is 38m
S28. Ans.(a)
Sol. Only (a) can be inferred from the given statement because it also described about the importance of immunization and its benefits. But (c), (d) and (e) cannot be inferred due to insufficient data given in the statement regarding it. Also (b) cannot be inferred as given statement suggest that one in ten children did not get vaccination.
S29. Ans.(d)
Sol. None of the statement can be assumed from the given statement. As it is given that the nothing is confirmed about the ultimate end of trash so (I) and (II) cannot be assumed. Also (III) and (IV) cannot be assumed as data related to this is not provided in the statement.
S30. Ans.(a)
Sol. Only (I) may be the reason as forest being the essential source of life so the warning is issued for its conservation. II shows the concern regarding the given statement but it is not the reason of the warning. Also, III contradicts the statement by stating that the forests are being managed more sustainably.
Solutions (31-35):
Final arrangement:
| Years | Age | Persons |
| 1985 | 39 | F |
| 1988 | 36 | L |
| 1989 | 35 | H |
| 1991 | 33 | K |
| 1992 | 32 | I |
| 1993 | 31 | D |
| 1994 | 30 | E |
| 1995 | 29 | C |
| 1999 | 25 | J |
| 2000 | 24 | M |
| 2002 | 22 | G |
Clues: L was born in Leap year. As many persons were born before L is same as were born after M. Four persons were born between M and I. The number of persons born before I is one more than the number of persons born after C.
Inference: Here we get three possible cases-
| Years | Age | Case 1 | Case 2 | Case 3 |
| Persons | Persons | Persons | ||
| 1985 | 39 | |||
| 1988 | 36 | L | I | M |
| 1989 | 35 | |||
| 1991 | 33 | |||
| 1992 | 32 | I | L | |
| 1993 | 31 | C | ||
| 1994 | 30 | M | I | |
| 1995 | 29 | C | ||
| 1999 | 25 | |||
| 2000 | 24 | M | L | |
| 2002 | 22 | C |
Clues: Sum of ages of C and D is multiple of 20. Age of E is more than J but less than D. J was not born in 2002. Sum of ages of L and G is 58. Sum of ages of F and H is more than the sum of ages of H and K. H is not oldest person but older than K.
Inference: Case 2 and Case 3 will be eliminated here-
| Years | Age | Case 1 | Case 2 | Case 3 |
| Persons | Persons | Persons | ||
| 1985 | 39 | F | ||
| 1988 | 36 | L | I | M |
| 1989 | 35 | H | ||
| 1991 | 33 | K | ||
| 1992 | 32 | I | L | |
| 1993 | 31 | D | C | |
| 1994 | 30 | E | M | I |
| 1995 | 29 | C | D | |
| 1999 | 25 | J | E | |
| 2000 | 24 | M | L | |
| 2002 | 22 | G | C | J |
Inference: The final arrangement is-
| Years | Age | Persons |
| 1985 | 39 | F |
| 1988 | 36 | L |
| 1989 | 35 | H |
| 1991 | 33 | K |
| 1992 | 32 | I |
| 1993 | 31 | D |
| 1994 | 30 | E |
| 1995 | 29 | C |
| 1999 | 25 | J |
| 2000 | 24 | M |
| 2002 | 22 | G |
S31. Ans.(b)
Sol. Except L, age of rest persons is even number.
S32. Ans.(c)
Sol. The one who was born immediately after D was born in 1994.
S33. Ans.(d)
Sol. Possible age of Z is 41 years.
S34. Ans.(e)
Sol. Six persons were born in between L and the one who was born immediately before M.
S35. Ans.(b)
Sol. K was born three persons after the one who was born just before L
| Related Posts | |
| Union Bank SO Syllabus | Union Bank SO Salary |
| Union Bank SO Previous Year Question Papers | |





 Inequality Tricks for Beginners, Easy Me...
Inequality Tricks for Beginners, Easy Me...
 Reasoning Questions for SBI Clerk Mains ...
Reasoning Questions for SBI Clerk Mains ...
 500+ Reasoning Questions PDF for SBI Cle...
500+ Reasoning Questions PDF for SBI Cle...









