Blood Relation Reasoning
Blood relation is an important topic of reasoning that is asked in the various competitive exams like SSC, Bank, Railways, and State Government Exams. Blood Relation evaluates candidates’ analytical and thinking abilities rather than just relying on calculations. To excel in blood relation questions, a clear understanding of family relations and basic concepts is required. The given article aims to provide insights into blood relation reasoning, step-to-step guide, example questions, and solutions, to help candidates in their preparation.
What Is Blood Relation?
Blood relation refers to the relationships between individuals acquired by birth, rather than through marriage or other means. Blood Relation Reasoning questions typically present a series of relationships, requiring candidates to deduce the relationship between two individuals based on the provided information. Analyzing familial ties among family members is crucial in solving the questions of Blood Relation. The male and female member relations that candidates will come across in the blood relation reasoning chapter have been discussed in the below table.
| Common Male and Female Member Relations | |
|
Male |
Female |
| Great grandfather, Maternal great-grandfather, Paternal great-grandfather, Great grandfather-in-law | Great grandmother, Maternal great grandmother, Paternal great grandmother, Great grandmother-in-law |
| Grandfather, Maternal grandfather, Paternal grandfather, Grandfather-in-law | Grandmother, Maternal grandmother, Paternal grandmother, Grandmother-in-law |
| Father, Uncle, Maternal uncle, Paternal uncle, Father-in-law | Mother, Aunt, Maternal aunt, Paternal aunt, Mother-in-law |
| Husband, Brother, Cousin, Brother-in-law | Wife, Sister, Cousin, Sister-in-law |
| Son, Nephew, Son-in-law | Daughter, Niece, Daughter-in-law |
| Grandson, Grandson-in-law | Granddaughter, Granddaughter-in-law |
| Great Grandson, Great Grandson-in-law | Great Granddaughter, Great Granddaughter-in-law |
The table below shows the relations as they asked in exams, the types of relations and their direct relations
| Relationships | |
| Relation | Name |
| Father’s/ Mother’s Son | Brother/ Myself |
| Father’s/ Mother’s Daughter | Sister/ Myself |
| Father’s Brother | Uncle/ Paternal Uncle |
| Father’s Brother’s Wife | Aunt/ Paternal Aunt |
| Mother’s Brother | Uncle/ Maternal Uncle |
| Mother’s Brother’s Wife | Aunt/ Maternal Aunt |
| Father’s Sister | Aunt/ Paternal Aunt |
| Mother’s Sister | Aunt/ Maternal Aunt |
| Father’s Father | Grandfather |
| Father’s Mother | Grandmother |
| Mother’s Father | Maternal grandfather |
| Mother’s Mother | Maternal Grandmother |
| Son’s Wife | Daughter-in-Law |
| Daughter’s Husband | Son-in-Law |
| Husband’s/ Wife’s Sister | Sister-in-Law |
| Husband’s/ Wife’s Brother | Brother-in-Law |
| Sister’s Husband | Brother-in-Law |
| Brother’s Wife | Sister-in-Law |
| Brother’s/ Sister’s Son | Nephew |
| Brother’s/ Sister’s Daughter | Niece |
| Uncle’s/ Aunt’s Son/Daughter | Cousin |
| Son’s/ Daughter’s Son | Grandson |
| Son’s/ Daughter’s Daughter | Granddaughter |
| Grandson’s/ Granddaughter’s Son | Great-Grandson |
| Grandson’s/ Granddaughter’s Daughter | Great-Granddaughter |
Blood Relation: Sides
There are two main sides to blood relations:
- Paternal Blood Relation: This pertains to relationships on the father’s side, including siblings, uncles, aunts, cousins, and grandparents (dada, dadi).
- Maternal Blood Relation: This involves relationships on the mother’s side, comprising similar familiar relationships such as siblings, uncles, aunts, cousins, and grandparents (nana, nani).
Blood Relation: Types
Blood relation reasoning questions assess the ability to analyze information about family connections and draw logical conclusions. The various types of questions for Blood Relation Reasoning are as follows:
- Direct Statements: These questions provide clear statements about relationships between family members. Candidates need to analyze these statements and answer a question based on the information provided.
Example: John is the son of Mary. Mary is the sister of David. How is John related to David?
- Coded Relationships: These questions use symbols or codes to represent family members (A, B, C etc.) and their relationships (+ for father-son, * for sister-brother etc.). Aspirants need to decipher the code based on the given statements and solve the question.
Example: A + B means A is the father of B. C * D means C is the sister of D. Statement 1: P + Q. Statement 2: S * T. Question: How is P related to T?
- Pointing/Introducing: These questions involve a person introducing or pointing to another family member. Students need to understand the description and analyze the generation and gender differences to determine the relationship.
Example: Pointing to a photo, a lady says, “This is the daughter of my husband’s son.” How is the lady related to the person in the photo?
- Family Tree: Sometimes, a question might provide a basic family tree with some relationships filled in. Candidates need to use the given information to deduce the remaining relationships.
These questions can get more complex by involving multiple generations, marriages, and in-laws. But by understanding the basic family structure and practising these different formats, you can develop strong reasoning skills to tackle any blood relation question thrown your way.
Blood Relation Reasoning: Step-to-Step Guide
The step-to-step guide for solving the blood relation questions has been discussed below. Aspirants facing problems in solving the questions must follow the tips for better understanding.
- Clear Understanding of Relations: It’s imperative to have a clear grasp of familial relations and common terms like spouse, sibling, aunt, uncle, etc. Understanding these relationships helps in understanding the information provided in the questions.
- Avoid Assuming Gender: Gender assumptions based solely on names should be avoided. For instance, if a statement mentions “A is the son of B,” B’s gender cannot be determined unless explicitly stated in the question.
- Pictorial Representation: Utilize diagrams or symbols tabulated below to visually represent relationships. This approach aids in understanding complex familial structures and clarifies the relationships between individuals.
- Practice: Regular practice is key to mastering blood relation questions. Engaging in practice sessions familiarizes candidates with various types of questions and enhances their problem-solving skills.
Blood Relation Questions, Answers & Explanation
Directions (1-3): Study the information carefully and answer the questions given below.
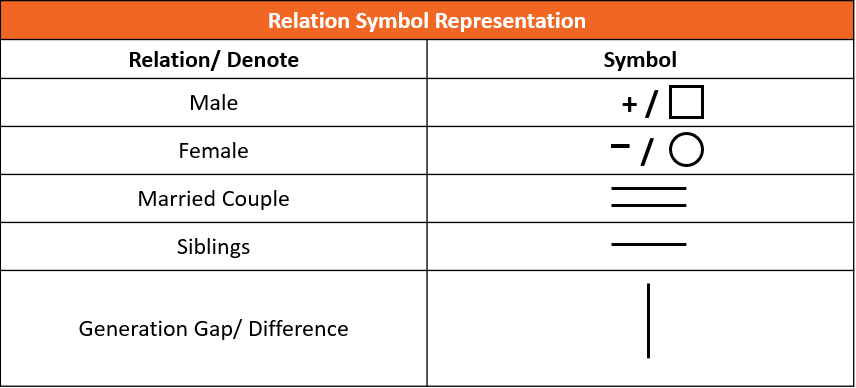
Eight persons are in three generations of family and two married couples. P is the son-in-law of H who has three children. M is the nephew of L. W is the father of K who is the sister-in-law of U. U is the only daughter of H who is the father of N. L is unmarried. N and K don’t have any children.
Q1. Who among the following is the son-in-law of W?
(a) U
(b) P
(c) N
(d) K
(e) None of these
Q2. Who among the following is the sister of N?
(a) P
(b) U
(c) K
(d) N
(e) None of these
Q3. How many male members in the family?
(a) Four
(b) Five
(c) Three
(d) Six
(e) Two
Directions (4-6): Each of these questions is based on the following information:
(i) A % B means A is the daughter of B.
(ii) A @ B means A is the mother of B.
(iii) A $ B means A is the father of B.
(iv) A * B means A is the son of B.
(v) A © B means A is brother of B
Q4. If the expression ‘D@E*K©L%O’ is true, then which of the following statement is true?
(a) O is grandmother of E
(b) L is uncle of E
(c) D is son-in-law of O
(d) E is granddaughter of O
(e) None is true
Q5. If the expression ‘L%N$T@U©X*Z’ then who among the following is son-in-law of N?
(a) T
(b) Z
(c) U
(d) X
(e) None of these
Q6. If the expression ‘H©F$E%K@R*F’ true, then which of the following is not true?
(a) R is nephew of H
(b) K is mother of E
(c) H is aunt of E
(d) K is sister-in-law of H
(e) All are true
Directions (7-9): Study the information carefully and answer the questions given below.
There are eight members in a family consisting of three generation and equal number of males and females. D does not belong to the youngest generation. F is father-in-law of J’s daughter. J is married to the daughter of N. M is maternal grandfather of B who is son-in-law of C. A is the daughter of C.
Q7. How is B related to C?
(a) son
(b) daughter
(c) son-in-law
(d) mother
(e) none of these
Q8. How is N related to A?
(a) father
(b) mother
(c) grandfather
(d) grandmother
(e) aunt
Q9. How many members are in the youngest generation?
(a) Two
(b) One
(c) Three
(d) Four
(e) None of these
Directions (10-11): Study the given information carefully and answer the given questions.
H has only two children-B and C. B is the sister of C. D is the son of C. E is the brother of D. F is the mother of E. G who is sister of D, is the granddaughter of A who is the mother of B.
Q10. How is A related to E?
(a) Grandmother
(b) Son
(c) Mother
(d) Cousin Brother
(e) None of these
Q11. How is G related to A’s daughter-in-law?
(a) Sister
(b)Mother
(c) Son
(d) Daughter
(e) None of these
Directions (12-15): Study the following information and answer the given questions.
There are nine members in three generations and three married couples in the family. There are only four male members in the family. Q is son of T who is the daughter-in-law of P. X is father of V. R is mother of S who is father of U. S is son-in-law of W. V is unmarried and aunt of U. X is not married to R.
Q12. Who among the following is Son-in-law of X?
(a) P
(b) S
(c) Q
(d) R
(e) U
Q13. How R is related to Q?
(a) Grandfather
(b) Father
(c) Sister
(d) Grandmother
(e) Brother
Q14. Who among the following is the nephew of V?
(a) Q
(b) S
(c) R
(d) P
(e) T
Q15. Which of the statement is false with respect to T?
(a) T is mother of U
(b) P is the father-in-law of T
(c) X is mother of T
(d) T is sister of V
(e) All are true
SOLUTIONS
Solutions (1-3):
Sol.
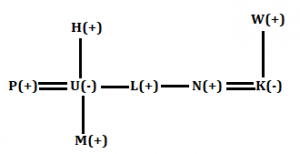
S1. Ans. (c)
S2. Ans. (b)
S3. Ans. (d)
Solution (4-6):
S4. Ans.(e)
Sol.
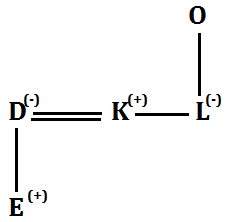
S5. Ans.(b)
Sol.
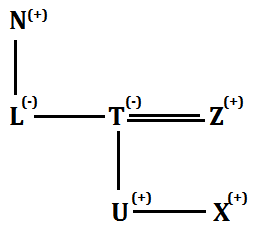
S6. Ans.(c)
Sol.
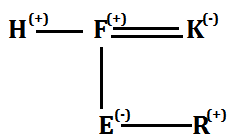
Direction (7-9):
S7. Ans. (c)
Sol.
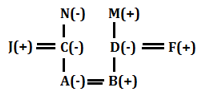
S8. Ans. (d)
S9. Ans. (a)
Solutions (10-11):
Sol.
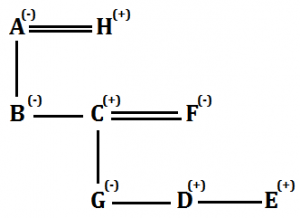
S10. Ans.(a)
S11. Ans.(d)
Solution (12-15):
Sol.
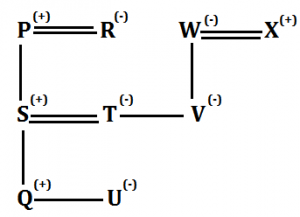
S12. Ans.(b)
S13. Ans.(d)
S14. Ans.(a)
S15. Ans.(c)




 GA Capsule for SBI Clerk Mains 2025, Dow...
GA Capsule for SBI Clerk Mains 2025, Dow...
 The Hindu Review October 2022: Download ...
The Hindu Review October 2022: Download ...
 SBI PO Syllabus 2025, Check Subject Wise...
SBI PO Syllabus 2025, Check Subject Wise...


